December 3rd, 2013

As an internet user, you’re able to do more, access more and store more online than you’ve ever been able to before. Unfortunately, that makes your data more valuable to criminals than it has ever been before. Because of this, malicious tools used to steal your log-ins or personal information are rapidly on the rise. Tim Wilson, of Dark Reading, reports that over the past month there have nearly 344-thousand new malicious websites discovered. These websites vary in their design and goal, but all of them are being used by hackers to steal your identity, data or money or to infect your computer.
On average, this means there are about 11,500 new malicious website springing up every day, which significantly increases the likelihood that a typical user will stumble across one of these sites. About 173-thousand of these websites have been identified as malware distributors. These sites often download malware to your computer without any action being taken on your part, beyond simply loading the website. Many times this download will take place in the background, which means it could be weeks or months before you learn that you’ve been infected.
About 114-thousand of the malicious websites were labeled as phishing sites. These sites attempt to steal users log-ins and passwords. Usually, they’ll use the name and logo of a familiar site to attempt to fool visitors into thinking they’re on a trusted page. Most often in these examples, PayPal was used to gain access to accounts and steal users’ money. There has also been a rise of site designed to steal users’ Google log-ins. This is attributed to the fact that one Google log-in can give an individual access to Gmail, Google Drive and Calendar, Google+ and more.
These increasing threats illustrate the need for effective security on any device you use to access the internet. For help putting the proper security precautions in place at home or at your place of business, contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335. If you have a device that’s been infected with malware, bring it in to one of your convenient locations.
November 29th, 2013

There are a number of precautions you need to take in order to stay safe online. From firewalls to updated antivirus software, there are plenty of tools that can prevent a disastrous cyber attack or data breach. These tools still don’t guarantee your safety, however. Even with precautions in place, it’s important to understand where the majority of threats come from and avoid them altogether with safe surfing techniques. Ron Johnson, of Business2Community, listed some of the most common causes of security breaches and how to avoid them.
Open WiFi networks are found nearly everywhere you go, but they’re far from secure. Any data you send over public WiFi is easily intercepted and stolen by a third party. This doesn’t mean you shouldn’t ever connect to public WiFi. It means you need to be extra careful about what sites you access while using this type of unsecured network. Viewing and reading websites likely won’t cause a problem, but don’t log-in to any online accounts or your password could be compromised.
Most users understand the dangers in giving other people their password, but sometimes even the most savvy users give out their log-in information without even thinking about it. For example, if you’re having difficulty with an account, a customer service representative might ask you for your password. This doesn’t necessarily mean they are going to misuse it, but it’s always a good idea to change passwords once you’ve told them to anyone, including a help desk. They might not always be as careful with your information as you would be. It’s also never a good idea to share accounts with others, even friends or family. If you want to allow another individual to access your account, change the password, give them the new log-in information, then change it again once they’re finished.
Downloading anything should be a decision that every user is cautious of. Even seemingly trusted websites can be compromised and a file you download could end up infecting your system with malware. If you’re prompted to download an application, like a media player, go to that player’s official website to download. Be sure to scan every file downloaded with your antivirus program before opening. As for email attachments, don’t download them unless you were expecting a file to be sent to you and you know exactly what it is.
Speaking of email, phishing scams are a popular method for stealing your information and hacking into your online accounts. These scams have grown more sophisticated. Often, an email will appear to be from a legitimate website where you hold an account. It will claim there’s been a problem and you need to log-in immediately, or download software, or even put in credit card information. If you have any questions about the legitimacy of these emails, contact the website or business directly, by phone if possible. There’s never a time when a business will email and need your credit card information.
By learning some of these common hacker tactics, you’ll be able to be smarter about your online habits and avoid potential threats.
If you’d like to improve security at your home or business to further safeguard from malware, phishing scams, hacking and more, contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 27th, 2013

There are a number of reasons to focus more on security for your mobile device, or the mobile device of your employees. For personal use, 7-percent of smartphone owners have been the victim of identity fraud, which is a substantially higher rate than the rest of the population. For businesses, about two-thirds use the bring your own device model, but only about 4-percent manage the company data their employees access with personal devices. In both of these examples, the issues stem from a lack of mobile security. Eyal Manor, of Information Week, writes that companies must focus on the data being accessed by employees, rather than the devices themselves, to improve security.
Many smartphone users don’t keep their apps and operating system updated, which opens security holes. Many don’t use a passcode either. There’s more and more mobile specific malware being introduced every day. These would be reasons to institute mobile device management, but when employees are using their personal devices, it’s difficult for more businesses to demand that type of access and control. Instead, here are three ways to improve security by focusing on the data being accessed, rather the individual device.
This tactic takes all of business-centric data stored on an employees device and locks it down in a special, encrypted area. Rather than putting controls on the entire device, companies are able to control only the encrypted area allowing them to ensure the safety of company data.
Users may not have strict security in place to restrict who can access their device, but for company information enhanced authorization can be installed so that data isn’t compromised in the case of theft or a lost device. Similar to containerization, only vital company data would be stored behind additional walls, which would require an employees log-in information to get through.
Regardless of the other safety measures taken to protect data, if it’s not encrypted, it isn’t safe. Hackers are continually evolving their tactics to get past enhanced security, so data theft remains a possibility. If your data is encrypted, however, you take added precautions that stolen data can’t be accessed by a third party, and won’t come back to damage your company. Remember that encryption is important both for stored data, and for data being sent between two parties.
For help improving the security of your company’s data, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 22nd, 2013

Cloud computing holds a number of advantages for businesses, but some are still apprehensive citing security concerns. Ricky Ribeiro, of BizTech Magazine, spoke with security expert Kurt Roemer, to uncover how companies can stay secure while using the cloud. Here’s a look at the most compelling information.
In order to properly secure your company’s data using an entirely physical infrastructure, your security budget has to be incredibly large. Because of this, security in the cloud is, in many ways, an improvement because it takes a smaller budget to put necessary security in place. A company needs to diagnose their security needs and speak to a professional cloud provider, who can manage their cloud services and provided the needed security.
A hybrid cloud set-up allows a business to use both a private cloud, which can be organizationally owned or managed by a cloud provider, and public cloud services. Security provisions must be in place in both the private and public cloud to keep sensitive data safe, whether it’s being stored or passed between clouds. To ensure security, connection points between the clouds need to be automated.
- Mistakes of cloud security
While cloud computing offers an alternative to the traditional data center, it can’t be managed the same way. When IT departments view the cloud the same way they’d view physical machines, it seems that private clouds are the only viable option. It’s true that the public cloud isn’t right for every application, but they can be used effectively in some situations to increase the cost-effectiveness of the cloud. Data security needs to be diagnosed to decide what is appropriate for the public cloud and what needs the added safeguards of a private cloud.
The downfall of cloud security comes in many forms that will be familiar to those with experience in traditional data centers. Weak passwords, account sharing and absence of encryption all lead to common security problems in the cloud. There are a number of protection options in the cloud to overcome these concerns, however. Multitenant administration, delegated responsibilities, distributed lifecycle management and security automation can all help you overcome typical user weaknesses.
If your business isn’t using cloud technologies yet, you’re falling behind your competition. To find out how cloud computing helps make your business more efficient, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 15th, 2013

It seems like every week a large-scale password theft makes headlines. The latest was Adobe, who experienced the loss of about 150-million user log-ins. Michael Santarcangelo, of CSO, writes that anytime a large batch of log-in information is stolen it jeopardizes the security of other businesses. There are three steps that should be taken in this event to keep your business secure.
- Check The Email Addresses
When an attack of this nature occurs, the compromised log-in information is made public. If you know where to look, you can look through the list of stolen log-ins for email addresses in your domain. This is important because if an employee had information stolen for one account, it significantly increases the likelihood that their other accounts could be compromised. This could lead an attack to your network. If you see one of your addresses in the list of compromised accounts, be sure to notify the owner of the address, then change their log-in information for your network.
Every password that was stolen is now in a hacker’s database. That means that any individual who uses the same or similar password as a user who had their account compromised is now in danger. Hackers will use these learned passwords to launch more informed, intelligent attacks on accounts. Check your company’s log-ins for similar passwords and get them changed immediately.
Be sure to explain to the affected employees why their account log-ins need to be changed and how a hacker could attack them. Giving them access to better information and training could prevent an attack in the future.
Few business owners understand that the loss of a large group of log-ins and passwords, such as the Adobe situation, could affect them also. Taking these precautions is labor-intensive, but necessary for security.
For help protecting your company from a devastating cyber attack, contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 8th, 2013

About a month ago, software company Adobe announced that hackers had gained access to passwords and log-in information for millions of accounts. Initially, the number of accounts affected was estimated to be around 38-million. As Jim Finkle reports at NBC News, that number is actually significantly higher.
Password security firm, LastPass, discovered the stolen customer data on a website for cyber criminals. In actuality, 152-million user accounts were compromised.
Adobe, which makes popular software like PhotoShop and Acrobat, downplayed the significance of the data breach. They claim many of the accounts who saw their log-in information stolen were inactive. Either the email or password was out of date, or the account was registered under false information in order to take advantage of one-time free use offers. The out of date log-ins total an estimated 43 million accounts. It’s unknown how many accounts were set up with fictitious information.
Still, Adobe has notified 38-million users that their accounts may have been compromised.
Regardless of whether the log-ins were up to date or not, security experts warn that the data stolen is still valuable to criminals. The data stolen can be used in phishing scams with relevant details included to make them more believable. There’s also the concern of Adobe passwords being used for other accounts. As one expert pointed out, a user may have registered with Adobe years ago and since let the account become dormant. However, they may use the same password for other online accounts, which a hacker could now have access to.
Some have suggested that Adobe didn’t do enough to safeguard customer’s data from an attack. While this is an example of what can happen when the proper security isn’t put in place at the business level, there’s also a wake-up call here for users. Regardless of how strong your password is, it’s still vulnerable. Hackers have a variety of ways of breaking into your accounts, and they don’t all involved brute force efforts to guess passwords. Also, failing to use unique passwords for each account leaves you much more vulnerable to hacking.
If you have a business that needs to improve your security to keep your data and your customer’s data safe from attack, or if you’d like to improve the security on your personal devices, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 5th, 2013

We’ve mentioned before that you can’t ever be completely secure online. But, some actions you take make you more secure and significantly less likely to be hacked. Andy O’Donnell of About suggests a number of mistakes that are commonly made and how they can lead to hacking. Here’s a list of some of the most common, as well as how you can avoid making them.
- Not Using Unique Passwords
Why would you need more than one password for your online accounts? If you use a long, strong password that’s difficult to break, you should be safe, right? Actually, no. Not all accounts are compromised by a third party guessing or breaking your password. Sometimes, large lists of passwords are stolen from companies. If your password is the same on every site you have an account with, a criminal could now have access to all those sites, rather than just the one. If you’re worried about remembering all of those unique passwords, consider using a password manager.
- Using An Unsecured Wireless Network
Whether it’s at home or at the office, your wireless network needs to be secured to keep out intruders. First, make sure you’re using adequate encryption. Check your router’s settings and enable WPA2 based encryption, rather than the less secure WEP. Then, set a long, strong password using upper and lowercase letters, symbols and numbers. Try to avoid using things like pets’ or children’s names or birth dates because those are likely to be known, or able to be found out, by others.
If you receive an unsolicited email with an attachment, don’t download the attachment. It’s simple advice, but many users believe they can download the attachment to find out what it is. In actuality, they’re downloading malware, which immediately infects their system. The same goes with pop-ups. Even with a pop-up blocker active in your web browser, you may see pop-ups from time to time, especially if you’re on a questionable website. Clicking on these pop-ups will often start a malware download.
To be properly secured, you need an active antivirus program and a firewall in place. These have to be turned on to work. This seems obvious, but many users will disable them if their computer is running slow, or if they’re having trouble running another application. This is ill advised. Also, security software needs to be continuously updated. This is to enable to software to recognize the latest pieces of malware and viruses. If you fail to update your antivirus, it becomes less and less effective.
These common mistakes make you an attractive target for hackers. To improve your cyber security, or to fix the damage already done to a device by malware and viruses, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 4th, 2013
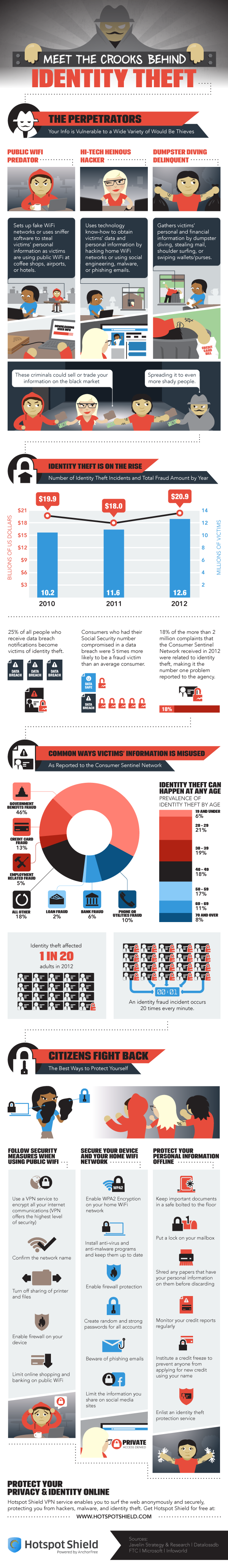
Protecting your computer from viruses and malware is only part of the concern of cyber security. Identity theft, which often begins with data being stolen over unsecure networks, through malware, or phishing scams, is also a costly threat.
Peter Nguyen, of the HotSpot Shield blog, writes that the number of identity thefts in the US is constantly growing. Last year, there were 12.6-million victims, which is enough for an identity theft to happen every 3-seconds. The financial loss of the victims totaled almost $21-billion.
The included infographic covers the how and why of identity theft. It also gives a few tips for how to stay safe. In addition to some offline measures, like shredding documents containing personal information, monitoring your credit reports, and locking your mailbox, here are the most important online safety tips.
- Beware public WiFi. When using an unsecured network at a coffee shop or other public place, limit your activity. Any transactions that require you to input financial information should wait. A firewall should be enabled on your device and you should turn off sharing of printers and files.
- Use proper security on your home wireless router. The router is your first line of defense, so make sure WPA2 encryption is enabled and a strong password is required to log on.
- Keep antivirus programs running in the background and keep them updated. Updating security software enables them to detect and protect against the latest threats.
- Keep social media profiles private. Every social network gives you options for what you share with whom. Make sure strangers don’t have access to information like your birthday, family information, phone number and employment history. This can all be used for identity fraud.
- Use long, strong passwords. Many security experts suggest passwords longer than 6-characters and using both upper and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols.
To improve the security of your devices at home, or at your business, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335. We not only fix devices, we also help keep them safe.
October 17th, 2013

Passwords are a constant object of concern for security experts. We’ve used this space previously to talk about the potential weakness of passwords to protect your online accounts. Robert Lemos, of Dark Reading, reports that the habits of users creating easily guessed passwords and an upgrade in hackers’ capabilities for breaking them have made password protection increasingly weak.
When creating passwords, even seemingly strong ones that include upper and lower case letters, numbers and symbols, most users still use similar passwords so they’re more memorable. This use of mnemonics makes passwords predictable.
Hackers have tools capable of brute force password guessing. These programs guess billions of possible password combinations until they’re able to gain access to an account. Some top of the line programs can guess about 1-billion passwords per second.
When a user’s password is predictable because of recurring habits, hackers are able to make intelligent assumptions about what your password will look like. That narrows down their list of possibilities considerably, making their password guessing tools even more effective.
Add that to how many websites don’t have ample security on their customers’ passwords. There have been multiple examples over the past year of hackers stealing huge lists of passwords in one attack. This not only gives them access to those accounts, but also gives them real world examples of the types of passwords typically being used.
These brute force attacks are actually fairly rare. Most criminals won’t take the time to launch an attack against a single account. For that, they prefer to use phishing scams and social engineering to get users to send them their passwords unknowingly.
Having a secure password is still important, but it’s even more important to understand where secure passwords will do you the most good. For example, banking sites usually put the most security on their users’ passwords and they’re very rarely compromised. Using a secure password for your bank account is a given, but you want to be sure not to re-use that account on a less secure site. That’s how many bank website’s are compromised. A user will use the same password on a site that isn’t very secure, then a hacker will steal a large number of passwords from the unsecure site and use them on more secure sites.
Using a password manager is one way to enable you to use unique passwords for each account, but never have to worry about forgetting them. However, even this method is hackable.
Although it’s probably impossible to be completely secure, avoiding phishing scams and social engineering and having strong passwords in place will serve you well.
For more information about how to keep your accounts and your computer safe, contact Geek Rescue. We not only fix devices that aren’t working right, we also protect them against future attacks.
October 7th, 2013

As previously mentioned, antivirus programs can’t be expected to fully protect your computer. Hackers produce hundreds of thousands of new malware every day and even the most up to date security software can’t possibly keep up.
That’s why it’s important to do your part and keep your machine out of harms way as much as possible. Shay Colson, of Information Space, has some tips on how to avoid malware and other potential threats online.
Just as in the forest it’s important to watch where you step, online it’s important to watch where you click. Most malware is downloaded to a computer when the user clicks on something they shouldn’t have. Particularly when you’re on a less reputable website, it’s important to avoid clicking on ads or links as much as possible. Also, make sure any security software you have installed is up to date. That way, if you do encounter malware, you’ll have the best chance of having it detected before it does any real damage.
The simple solution for making all of your accounts online more secure is to improve your password. Make sure it is 8-characters or longer and includes both upper and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. Some advocate using your least secure passwords for throwaway accounts, medium passwords for social media, but if you want to avoid a potential hacking, use unique, strong passwords for each account. Using all of those different passwords can get confusing, so it’s also a good idea to use a password manager.
Almost everyone makes purchases online. It’s a good idea to use a credit card, rather than a debit card, however, since it’s easier to dispute fraudulent charges on a credit card. Most eCommerce sites give you the option to save payment information for your next purchase. This is a time saver, but it puts your account information at risk. It’s much better to enter your card number each time than have it available to anyone who gains access to your account.
Your mobile device also has access to sensitive data. Keep it safe by utilizing the lock screen. As seen with an iOS bug that allowed users to bypass the fingerprint scanner, or Android’s notoriously easily hacked lock, this doesn’t fully protect your device. However, it offers some protection and is easy to use. Also, be sure to enable services to remotely disable and wipe your phone in case it’s stolen. Both Apple and Android offer this service. It’s extremely useful in keeping your data out of a criminal’s hands.
These tips keep your information safe without installing additional security software. However, you should always have antivirus programs and other security in place. To improve the security on any of your devices, contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335. We also remove viruses and other malware from infected machines.




















