November 8th, 2013

One of the most common complaints about Google’s popular web browser, Chrome, is its inordinate number of security vulnerabilities. As Gregg Keizer reports for Computer World, Google is doing its part to close up one of the most noticeable flaws in its security by no longer allowing the installation of extensions that aren’t in the Chrome Web Store.
Currently, users can browse the Chrome Web Store for extensions, which other browsers call add-ons, much the same way you would browse for apps on your smartphone. These extensions grant the browser additional capabilities. Extensions have also been found outside of the Web Store. Some third party vendors offer Chrome extensions directly on their site’s, or included in downloads of their applications. Some companies have even engineered their own extensions specifically for their employees. Under Google’s new rules, these third party extensions would no longer be accepted by Chrome browsers.
The reason for this move is that it keeps users from accidentally downloading malicious extensions. By limiting users to only installing extensions from the official Web Store, Google is able to police all extensions available and remove those that contain malware or act maliciously.
Android hasn’t yet made the same move to limit users to only apps found in the Play store, but they do recommend that users stick to those apps. Otherwise, users risk infecting their devices with apps that haven’t been officially approved by Google.
This move for Chrome has been in the works for some time. When Chrome 21 launched in 2012, it no longer accepted extensions installed directly from a third party website. Earlier this year, Chrome again tightened extension security by adding a feature that blocked silent installations of extensions and disabled those already installed. This closed a vulnerability that allowed hackers to install extensions without a users knowledge. Usually, this was done in response to another user action to download from an untrusted source.
In order to completely close any remaining loopholes, Chrome has now gone to a strict policy of only allowing extensions directly from the Web Store. That doesn’t mean, however, that independent developers, and those developing extensions for company use, can’t continue to use their own extensions. The Web Store offers an option to hide extensions from the public and only make them available to those they’re intended for. Extensions will also still be available to download directly from third party sites, as long as the same extension has also been added and approved in the Web Store.
These changes aim to make Chrome a more secure browser. To upgrade your security at home or at the office, contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 7th, 2013

What do you know about threat feeds? These are a real time warning system that allow security teams to take necessary precautions to prevent the latest threats. They can be an incredibly useful resource for protecting your business. As Eric Ogren, of Computer World, points out, however, you may not have the necessary resources to adequately use threat feed. Instead, they might be best left to a third party vendor who handles your security.
- Find Threats Specific To Your Business
A threat feed isn’t tailored to you specifically. Instead, it’s a broad view of the latest threats in the wild. So, part of the investment involves combing through these feeds with a knowledge of your IT infrastructure and being able to recognize the threats that pose the biggest danger to you. This takes time and a high level of expertise. If you have both of these, a threat feed can serve you well. If you don’t, you’ll probably be better served letting a third party handle it.
- Developing Your Own Protection
Once you’ve discovered threats that are dangerous to you, you’ll want to protect against them. That means developing your own anti-malware signatures and patching your own security. These are the same types of actions an antivirus program would take, but you’ll be able to roll them out faster. That is, if you have the resources and knowledge available.
- Do You Have The Resources?
As mentioned, threat feeds present an opportunity to stay ahead of cyber attacks by recognizing the latest threats to your business. You have to have the capabilities to not only identify these threats, however, but also to take action to prevent them. If your team is capable, threat feeds should become a staple of your security.
If you’d like to leave your company’s security in the hands of the professionals, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335. We’re equipped to protect you against the latest threats and keep your data secure.
November 6th, 2013

If you have an Android smartphone, you’ve probably noticed that there are a number of apps that came pre-loaded on it that you don’t need and don’t use. These apps come from the phone’s manufacturer, but as Liam Tung of ZDNet writes, they may be creating vulnerabilities in your smartphone’s security.
Researchers at North Carolina State University examined pre-installed apps on smartphones made by Google, Samsung, HTC, LG and Sony. Of the 10 devices studied, 86-percent of pre-loaded apps requested more permissions than they actually used. This gives the apps access to data they don’t need, but that data becomes accessible when the app is compromised.
In terms of sheer number of vulnerable, pre-installed apps, the HTC Wildfire S and the Samsung Galaxy S2 had the most of the pre-2012 devices. For post 2012, the Samsung Galaxy S3 contained a stunning 40 vulnerabilities. In contrast, Google’s Nexus 4 only had three vulnerabilities.
Google itself has a good track record for releasing security patches to fix vulnerabilities found on their hardware. However, for individual manufacturers like Samsung, Sony and HTC, these patches take time to roll out to customers. For the devices studied, an average of 6-months is how long it took for an officially released security patch to finally make it to all affected customers. That amount of time leaves a large window for hackers to exploit those vulnerabilities.
Some of these native apps are able to be removed by users, but many others cannot be. This means users stay at risk until an appropriate security patch is released to fix the problem. So, next time you’re in the market for a new Android smartphone, be sure to consider how many pre-installed apps it comes with.
At Geek Rescue, we remove malware, fix broken hardware and improve security on all kinds of devices, including smartphones. Whatever your issue, call us at 918-369-4335 or stop by one of our locations.
November 5th, 2013

We’ve mentioned before that you can’t ever be completely secure online. But, some actions you take make you more secure and significantly less likely to be hacked. Andy O’Donnell of About suggests a number of mistakes that are commonly made and how they can lead to hacking. Here’s a list of some of the most common, as well as how you can avoid making them.
- Not Using Unique Passwords
Why would you need more than one password for your online accounts? If you use a long, strong password that’s difficult to break, you should be safe, right? Actually, no. Not all accounts are compromised by a third party guessing or breaking your password. Sometimes, large lists of passwords are stolen from companies. If your password is the same on every site you have an account with, a criminal could now have access to all those sites, rather than just the one. If you’re worried about remembering all of those unique passwords, consider using a password manager.
- Using An Unsecured Wireless Network
Whether it’s at home or at the office, your wireless network needs to be secured to keep out intruders. First, make sure you’re using adequate encryption. Check your router’s settings and enable WPA2 based encryption, rather than the less secure WEP. Then, set a long, strong password using upper and lowercase letters, symbols and numbers. Try to avoid using things like pets’ or children’s names or birth dates because those are likely to be known, or able to be found out, by others.
If you receive an unsolicited email with an attachment, don’t download the attachment. It’s simple advice, but many users believe they can download the attachment to find out what it is. In actuality, they’re downloading malware, which immediately infects their system. The same goes with pop-ups. Even with a pop-up blocker active in your web browser, you may see pop-ups from time to time, especially if you’re on a questionable website. Clicking on these pop-ups will often start a malware download.
To be properly secured, you need an active antivirus program and a firewall in place. These have to be turned on to work. This seems obvious, but many users will disable them if their computer is running slow, or if they’re having trouble running another application. This is ill advised. Also, security software needs to be continuously updated. This is to enable to software to recognize the latest pieces of malware and viruses. If you fail to update your antivirus, it becomes less and less effective.
These common mistakes make you an attractive target for hackers. To improve your cyber security, or to fix the damage already done to a device by malware and viruses, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 5th, 2013

Spam is everywhere online. An estimated 14.5-billion messages categorized as spam are sent every day. It’s not just your email inbox that’s being bombarded either. Comment sections, social media and even text messages are also being hit. A post at the All Spammed Up blog writes that we only have ourselves to blame for this barrage of spam.
Electronic spam is an umbrella term that refers to any unsolicited, mass message usually used for advertising purposes. It’s the online equivalent of junk mail addressed to ‘Resident’. Recently, it’s also been adapted to spread malware. The reason it exists and is expanding is that it works. Those who are sending out spam messages are finding it to be a worthwhile endeavor and a profitable one. The key to stopping it is for users to get smarter and stop falling for it.
Messages pour into your email every day and most of them are caught by a filter and placed in the spam folder. Still, some spam gets through to your inbox. Your phone even receives spam text messages, although not nearly as many as your email sees. The reaction of most people is to delete the obvious spam, but it keeps coming because there are those that don’t. You can’t control what other people do, but you can control how often you give out your contact information. If you want to stop spam from coming to your phone, stop giving out your phone number so indiscriminately. If you want to stop, or at least decrease spam email, be more careful who you give your address to. For any site you feel is questionable, use an alternate email instead of your primary address.
Spam on social media is a slightly different animal. The spam often comes from seemingly legitimate accounts of friends that have been hijacked. There are also dedicated phony accounts whose sole purpose is to send out spam and malicious links. Sites like Twitter and Facebook do take down phony accounts when they find them. If users stop clicking on these links, those spam accounts would disappear. To keep accounts from being hijacked, users need to surf safer. Accounts can be hacked in a number of ways, but usually it stems from clicking a bad link or downloading malware.
The comment sections of blogs, news sites and social media sites like YouTube and Instagram are often home to spam messages. They’re easy to distinguish from legitimate comments because they usually don’t have anything to do with the page their commenting on and almost always include a link. But, they use social engineering to entice users into following the link. Common tactics are promising high paying, work from home jobs, or cheap electronics. Most users know better, but follow the link to find out for sure whether it’s a legitimate offer. Blog and website owners usually delete these spam comments when they see them, but the spammers often combat this by including a compliment of the site and playing of the owner’s ego.
If no one fell for these spam messages, spammers would stop using these tactics, but probably evolve into something else. The keys for avoiding spam is to surf safely, have a trusted spam filter in place on email, resist offers that are too good to be true and generally be wary of links.
Geek Rescue offers protection from spam and malicious websites with out Safety Net program. We also clean and fix computers that are infected with malware. Call us at 918-369-4335 or stop by one of our convenient locations today.
November 4th, 2013
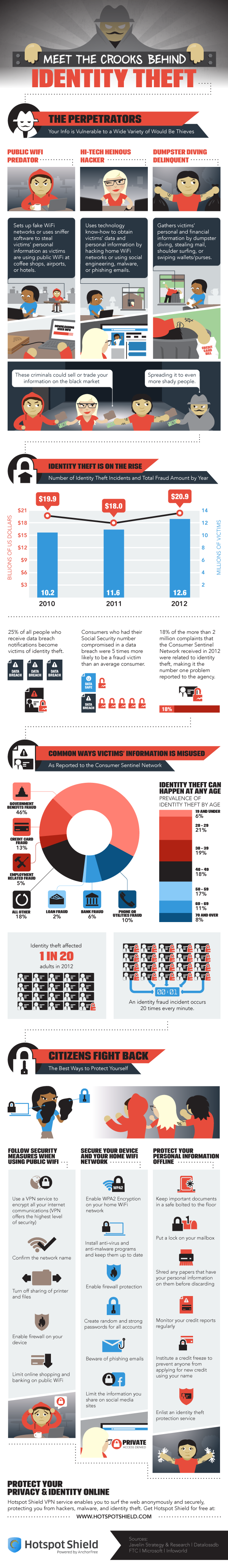
Protecting your computer from viruses and malware is only part of the concern of cyber security. Identity theft, which often begins with data being stolen over unsecure networks, through malware, or phishing scams, is also a costly threat.
Peter Nguyen, of the HotSpot Shield blog, writes that the number of identity thefts in the US is constantly growing. Last year, there were 12.6-million victims, which is enough for an identity theft to happen every 3-seconds. The financial loss of the victims totaled almost $21-billion.
The included infographic covers the how and why of identity theft. It also gives a few tips for how to stay safe. In addition to some offline measures, like shredding documents containing personal information, monitoring your credit reports, and locking your mailbox, here are the most important online safety tips.
- Beware public WiFi. When using an unsecured network at a coffee shop or other public place, limit your activity. Any transactions that require you to input financial information should wait. A firewall should be enabled on your device and you should turn off sharing of printers and files.
- Use proper security on your home wireless router. The router is your first line of defense, so make sure WPA2 encryption is enabled and a strong password is required to log on.
- Keep antivirus programs running in the background and keep them updated. Updating security software enables them to detect and protect against the latest threats.
- Keep social media profiles private. Every social network gives you options for what you share with whom. Make sure strangers don’t have access to information like your birthday, family information, phone number and employment history. This can all be used for identity fraud.
- Use long, strong passwords. Many security experts suggest passwords longer than 6-characters and using both upper and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols.
To improve the security of your devices at home, or at your business, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335. We not only fix devices, we also help keep them safe.
November 4th, 2013

What do you know about CrytpoLockers? As a post on the Integral IT blog reports, this relatively new form of computer virus is capable of gaining access to and encrypting files on your machine, which then makes it impossible for you to use them. In order to stay safe and minimize the damage, there are some precautionary steps that need to be taken.
CryptoLockers primarily gain access to your computer or network through email. They appear as a seemingly legitimate attachment. Once downloaded, they begin to wreak havoc.
Any file you have access to, a CryptoLocker will encrypt and damage. You’ll no longer be able to access these files. When you try to open them, you’ll be met with a warning that the file is corrupted and can’t be opened.
This warning is the first sign that you’ve downloaded a virus. Otherwise, the CryptoLocker operates in the background and is undetectable for most users.
To remove the virus, you’ll have to identify the file containing the CryptoLocker and delete it. Then, you’ll be able to restore the corrupted files from back-up, which you’ve hopefully kept current.
To avoid a catastrophic loss of data due to a CryptoLocker infection, keep a trusted, frequently updated antivirus program running on your machine. Allowing it to update constantly makes it more capable of detecting new threats like CryptoLockers before they do any real damage.
Be aware of threats like this when checking your email. Using attachments is a popular method of hackers for infecting a large number of users. Knowing this makes you more suspicious of emails containing attachments, especially when they’re unsolicited.
This is also a warning to keep your back-ups current and frequent. You’ll never be able to be immune to threats like this, so regularly backing-up vital files ensures that, even when disaster strikes, you’ll be able to recover quickly.
Geek Rescue offers security solutions for all of these issues and concerns. We remove existing viruses and malware, improve your security infrastructure to better protect against threats and offer data storage and back-up. Call us at 918-369-4335 to stay safe from threats like CryptoLockers.
November 1st, 2013

Google Chrome is the most used internet browser in the US. Users have long complained that it lacks some basic security features that would make browsing much safer. Juan Carlos Perez, of InfoWorld, reports that Google is attempting to make the Chrome experience safer by adding a tool that would block malware from being downloaded.
Chrome already contains options to be alerted when visiting an insecure, or potentially malicious, website. This new malware blocking tool would offer a similar alert from the download tray when a malware file is blocked from being downloaded.
Users encounter a shocking amount of malware online. Some download it thinking it’s something else, while other times the malware is automatically downloaded after clicking a link or landing on a site. As of now, Chrome offers no way of stopping these malicious or accidental downloads.
So far, there’s little else known about Chrome’s malware blocking tool. It isn’t widely available yet. Google plans to an early version of their Chrome Canary browser, which is meant for developers and other tech-savvy users. It’s speculated that should the tool prove to be valuable, it will roll out to all Chrome browsers.
Even with a malware blocker in place in your web browser, you computer is still at risk. Other security measures are needed to protect you from other threats. Without seeing Chrome’s malware tool in action, it remains to be seen how it integrates with other security programs.
Geek Rescue offers a range of security options to keep your devices secure. We also eliminate malware and viruses. Come by or call us at 918-369-4335.
October 31st, 2013

There have been relatively few true threats to the security of iPhones compared to the amount of malware being produced for Android. A serious threat has recently emerged, however. Antone Gonsalves, of Network World, reports that a team of security experts uncovered a vulnerability in a large number of iOS apps. The flaw allows for a third party to intercept data and then send their own directly onto a user’s device.
The team is calling it “HTTP Request Hacking” because it allows hackers to intercept HTTP traffic between the app and server. The hacker can then tell the app to retrieve data from a different server, which usually involves putting malicious links on your iPhone and iPad. This method is particularly effective for news apps because the hackers can put fake links in the news stories, which cause malware to be downloaded when clicked.
Once a hacker gains control of the app, they can continue to send whatever data they want until the app is updated to close the security gap, or removed completely.
There is such a large number of affected apps that the security team couldn’t contact all of them directly. Instead, they opted to spread the word through the media. The vulnerability only affects apps using an HTTP connection. Most high quality apps use the more secure HTTPS connection.
There’s code available to fix the problem, but it’s much easier to just remove the app. If it’s using an HTTP connection, you probably shouldn’t be using it anyway.
This particular security flaw was specifically found for iOS and while it hasn’t been tested on Android, security experts note that it’s likely that would affect those users as well.
If you believe you have malware infecting any of your devices, come by or contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335. We will fix your phone, tablet or computer and help make sure you’re prepared for the next malware attack.
October 30th, 2013

The Windows XP operating system was initially released in 2001. More than twelve years later, it still accounts for about a fifth of the operating systems in use on machines. This wouldn’t necessarily pose a problem, except that, as Kelly Jackson Higgins reports for Dark Reading, XP users are at a much greater risk of malware infections and Microsoft is cutting off support on April 8th, 2014.
While Windows 8 users and XP users encountered about the same amount of malware in the first half of 2013, XP machines were about six times more likely to be infected by attacks. Because the OS is so old, hackers have had more than a decade to develop malware for it and find security vulnerabilities. This means that malware attacks are likely to be highly effective because they specifically target known flaws. It’s also likely that users still using XP have not kept it updated properly. Many are likely behind on security patches and may not be running the latest antivirus programs either.
Security experts chalk up the high number of users stuck on XP to its familiarity. While Windows 7 and 8 have focused on better functionality, they’re also quite a bit different from XP. Instead of learning the ins and outs of a new OS, many users choose instead to stick with what’s comfortable.
So, what are these XP users risking? There are 3 types of malware that target these users the most. All are fast spreading worms that infect computers then spread to others.
- Sality- Steals personal information, changes security settings on infected machine
- Ramnit- infects Windows executable files, Office files and HTML files
- Vobfus- downloads other malware and spread with a USB flash drive
On April 8th, Microsoft won’t completely end support for Windows XP. But users will have to pay for a premium service for critical updates.
Geek Rescue cleans malware infections and fixes all of your devices. Bring your device by one of our locations or call us at 918-369-4335. If it boots up or turns on, we fix it.




















